- Cloud Database Insider
- Posts
- Amazon prematurely sends layoff notices😕|ScyllaDB🆚DynamoDB|Iceberg and Trino transform Data Lakehouses⚡
Amazon prematurely sends layoff notices😕|ScyllaDB🆚DynamoDB|Iceberg and Trino transform Data Lakehouses⚡
Data Federation vs. Data Virtualization vs. Lakehouse Federation
What’s in today’s newsletter:
Amazon prematurely sends layoff notices, causing employee confusion 😕
Iceberg and Trino transform Data Lakehouses ⚡
Also, check out the weekly Deep Dive - Data Federation vs. Data Virtualization vs. Lakehouse Federation
Want to get the most out of ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is a superpower if you know how to use it correctly.
Discover how HubSpot's guide to AI can elevate both your productivity and creativity to get more things done.
Learn to automate tasks, enhance decision-making, and foster innovation with the power of AI.
AWS

TL;DR: Amazon mistakenly sent early layoff notices to US and Canadian employees, causing confusion. The company acknowledged the error, highlighting challenges in cross-region workforce reductions and the need for better communication.
Amazon mistakenly sent early layoff notices to employees in Canada and the US, causing confusion and distress.
The company clarified that the layoff process was not yet finalized, acknowledging the premature alerts were errors.
This incident exposes challenges in managing workforce reductions across multiple regions with differing labor laws.
Premature notifications risk damaging employee trust and may push Amazon to improve communication protocols during layoffs.
Why this matters: Amazon’s premature layoff alerts risk eroding employee trust and morale, complicating an already sensitive restructuring. This incident underscores the challenges of managing cross-border workforce changes and highlights the crucial need for precise, transparent communication to uphold company reputation and employee relations in turbulent times.
NOSQL

TL;DR: ScyllaDB's new release offers 50% cost savings and faster scaling over DynamoDB, with a Seastar C++ architecture and flexible deployments, challenging AWS's dominance in cost-effective, high-performance NoSQL databases.
ScyllaDB’s new release offers a 50% cost reduction and faster scaling compared to Amazon’s DynamoDB.
The database utilizes a Seastar-based C++ architecture to improve throughput, latency, and resource efficiency.
It supports flexible deployment on both cloud environments and on-premises with lower operational overhead.
This launch challenges DynamoDB's market dominance, encouraging enterprises to explore more cost-effective NoSQL options.
Why this matters: ScyllaDB’s new release delivers faster, more cost-efficient scalability than DynamoDB, disrupting the NoSQL market. Lower costs and improved performance empower businesses to optimize cloud spending without sacrificing speed, promoting competition and innovation that could drive down prices and increase options for enterprise-grade database solutions.
DATA ARCHITECTURE

TL;DR: Apache Iceberg and Trino together advance data lakehouse architecture by ensuring reliable large dataset management and fast SQL querying, enabling scalable, cost-effective, and unified analytics for enterprises.
Apache Iceberg offers schema evolution, partitioning, and ACID transactions for reliable large dataset management.
Trino delivers interactive, low-latency SQL querying on Apache Iceberg tables across multiple storage systems.
The integration of Iceberg and Trino enables scalable, flexible data lakehouse architectures with unified analytics.
This combined architecture reduces costs and complexity while improving data governance and accessibility for enterprises.
Why this matters: The integration of Apache Iceberg and Trino revolutionizes data management by enabling scalable, reliable, and fast analytics within data lakehouses. This reduces operational costs and complexity while enhancing data governance and accessibility, empowering enterprises to harness unified, high-quality insights for competitive advantage across diverse industries.

EVERYTHING ELSE IN CLOUD DATABASES
Databricks, Anthropic, Figma eye 2026 IPOs
Top 10 Data Lake Startups to Watch in 2026
Top 10 Best Practices for Amazon EMR Serverless
BigQuery Integrates Huggingface SQL Models
Datadog Leads AI-Driven Observability Revolution by 2026
Endee.io Launches Open-Source AI Vector Database
Kenya's first public cloud launched by IXAfrica & Oracle
AWS Unveils DynamoDBSaver for LangGraph AI Agents
BigQuery adds AI-powered conversational analytics
Google BigQuery Adds Vibe Querying Feature
Databricks Unveils AI Assistant for Enterprise Docs
ClickHouse boosts vector search with HNSW index
Snowflake Connector Boosts Data Transfer Efficiency
Snowflake’s Pantomath boosts data operations power
Spanner 2025: Next-Gen Global Database Unveiled
Neo4j's Graph Data Science boosts AI insights
Neo4j updates: Twin4j, Cypher & graph tools news

DEEP DIVE
Data Federation vs. Data Virtualization vs. Lakehouse Federation
This section is inspired by some real world work that I have been doing in the last 8 weeks or so. I would love to give you the full details, but as I have stated before, I have to be judicious in what I write here as to not contravene any privacy agreements and convey any proprietary information.
What I can say is that there are widely understood data architectures that with the proliferation of all the platforms and tools you can find covered in the newsletter, there has to be an agreed upon way of accessing data in a secure an performant manner.
Other considerations that we should consider when putting together data from disparate systems are the minimization of data movement and the goal to minimize the proliferation of new tools.
This is where the notion of Data Federation, Data Virtualization, and Lakehouse Federation come into play.
Data Federation can be defined as an architecture that several distinct databases to function as a single logical entity. The core characteristics are:
Virtual Unification
Zero-Copy Approach
Source Autonomy
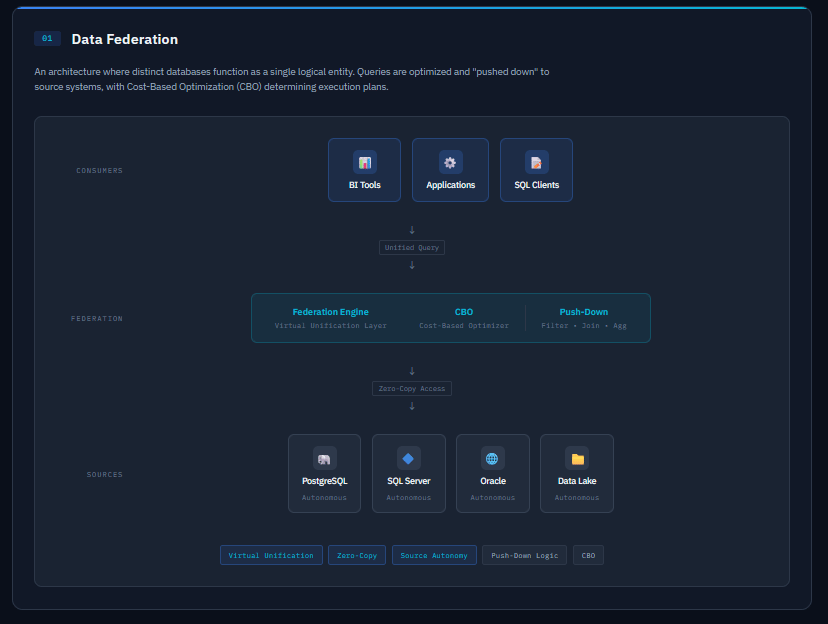
One of the key technical points of data federation are Push-down Logic. This is a process where filtering, aggregation and join are are “pushed-down” to the source system.
The querying system uses Cost-Based Optimization (CBO) to determine the most efficient execution plan. This is based on the data and statistics of the source system.
Data Virtualization is a data integration and management architecture that creates a logical abstraction layer. It is strategy that wraps federation with semantic modelling, caching, and governance.
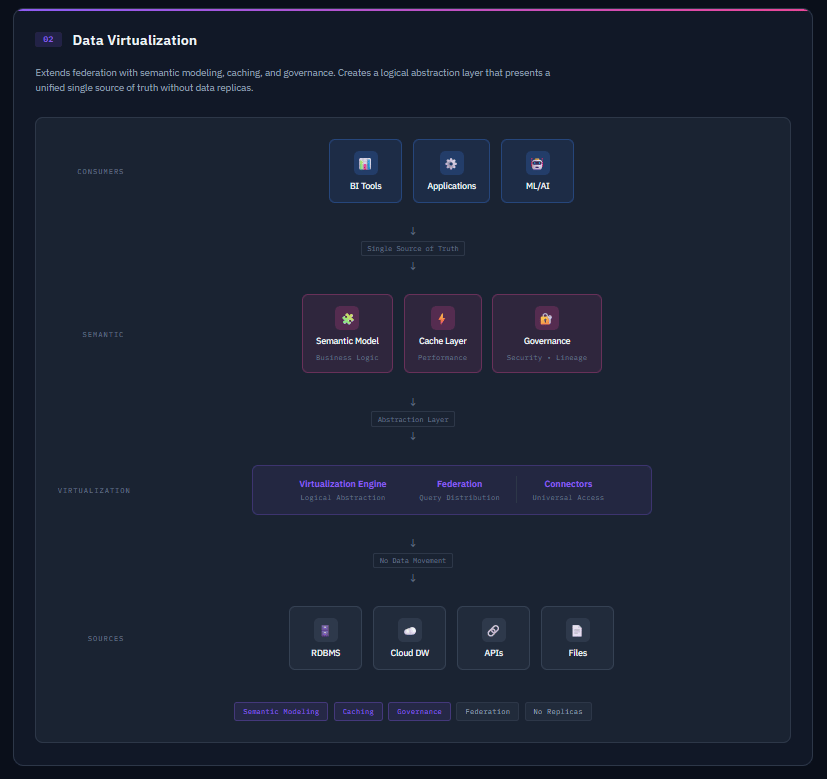
Data Virtualization decouples the consumption of data from its physical storage and format, and presents a unified single source of truth without creating data replicas.
Lakehouse Federation is an architecture that extends the Data Lakehouse to access, query, and govern external data sources.
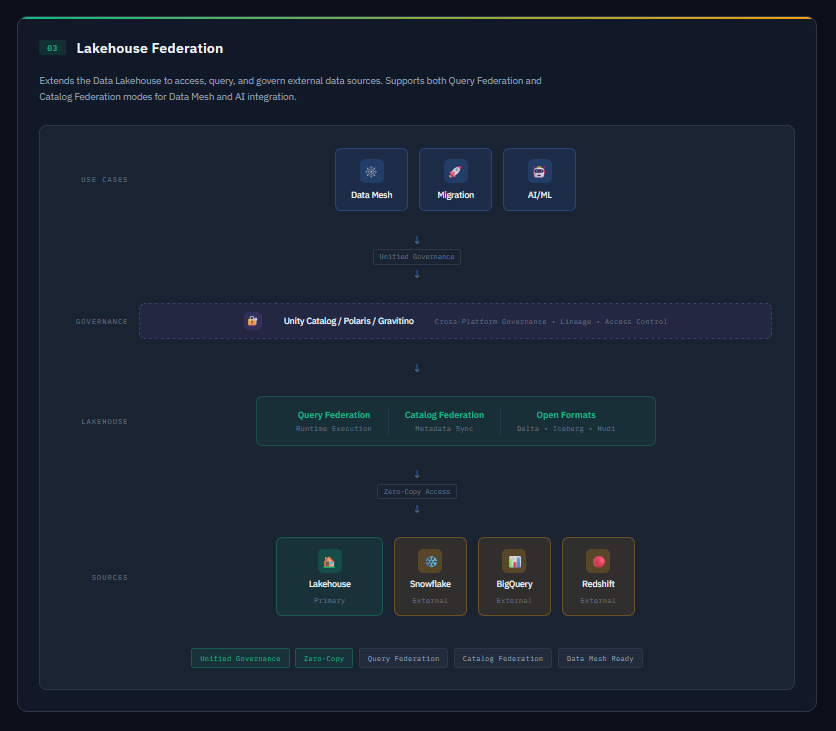
The core architectural principles of Lakehouse Federation are:
Unified Governance
Zero-Copy Access
There are two technical execution modes, Query Federation and Catalog Federation.
The strategic value of Lakehouse Federation are:
Data Mesh Implementation
Migration Acceleration
AI Integration
Note that these three concepts exist on a spectrum rather than being entirely distinct. Data Virtualization encompasses federation, and Lakehouse Federation is essentially federation applied within the lakehouse paradigm.
I could write several newsletter editions and multiple blog posts about these 3 architectures, but a condensed and synthesized post is found here with everything that you can read at your leisure.
Gladstone Benjamin

